Selenium is the 34th element on the periodic table with the chemical symbol Se. The element is nonmetal and has similar properties to tellurium and arsenic. Following is the atomic structure of selenium.
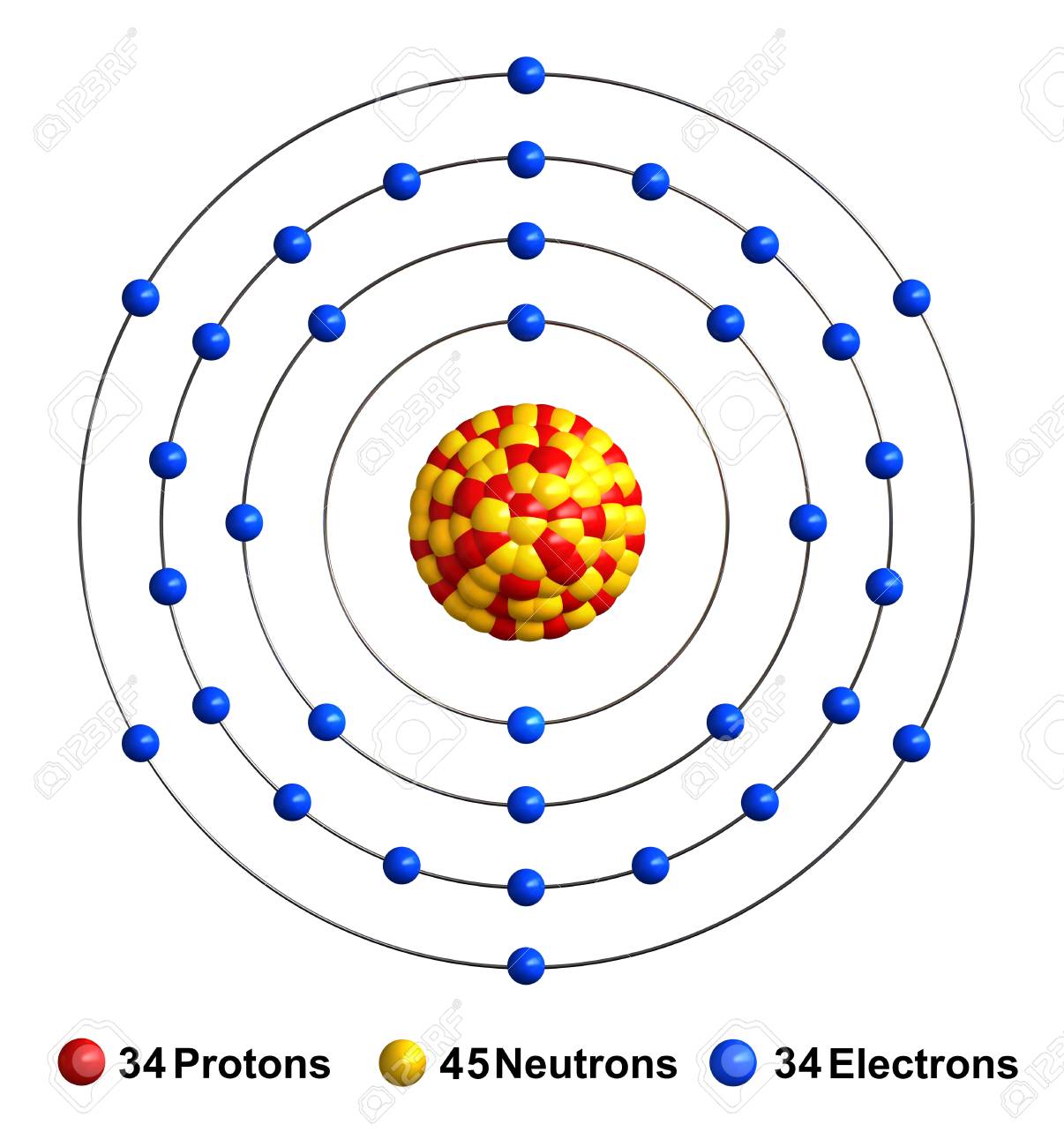
Atomic Structure of Selenium
As Figure – 1 shows, selenium has 34 protons and electrons and 45 neutrons. The electrons of the element are orbiting the nucleus, distributed in the division of 2, 8, 18, and 6 in four orbits.
Selenium is an important mineral for our body, as it is vital in a number of health functions. It is taken primarily through diet but is only needed in a small amount. Still, there is a range of functions that require selenium to work properly. If the amount of selenium in our diet is not adequate, it can lead to selenium deficiency.
Food Sources for Selenium

Picture By Yukiko Kanada at Unsplash
Selenium is found in a range of sea, plant, and meat sources.
- Oysters are a great source of selenium. 3 ounces (85 grams) of oysters contain 238 percent of the daily value of selenium required.
- Chicken breasts also have selenium. 84 grams of chicken breast contain 12 percent of the daily value of selenium.
- Yellowfin tuna provides 167 percent of the daily value in just 3 ounces (85 grams).
- Brazil nut is also an excellent source of selenium where a single nut of 5 grams provides 174 percent of the daily value.
Other than that, eggs, sunflower seeds, shiitake mushrooms, sardines, and halibut also provide selenium to the body when used in the diet.
Selenium Deficiency
Selenium Deficiency is a condition where the amount of selenium intake in the body is not enough to replenish the various systems relying on dietary intake of the element. This can lead to a range of health issues.
Processes Affected
In selenium deficiency, the major processes that get affected include the following:
- Infection protection
- Reproductory system
- Synthesis of DNA
- Thyroid hormone metabolism
How much selenium is found in a person’s food depends largely on whether the quality of the soil in which the food is grown is up to the mark or not. The concentration of selenium in the soil largely depends upon the pH levels, evaporation, and rainfall in the area. That is why selenium deficiency is more common in some places than others.
According to a study, selenium deficiency is not as big of a problem in the United States but affects over 1 billion people all across the world. As climate change gets worse, selenium deficiency is also projected to increase due to weather conditions causing detrimental soil conditions in various parts of the world. That is predicted to be a big problem in the southwestern United States.
Latest studies have indicated that selenium deficiency may exacerbate the symptoms of Covid-19. A systematic review by Mohammad Fakhrolmobasheri and his team concluded that selenium deficiency resulted in severe cases of Covid-19 in most cases and recommended selenium supplementation for Covid-19 patients.
Symptoms of Selenium Deficiency
The most common symptoms of selenium deficiency have been outlined as follows:
- Weak immune system
- Hair loss
- Mental fog
- Fatigue
- Muscle weakness
- Infertility in women and men
These symptoms can manifest themselves at different ages but one of the most prominent things common in these conditions is a distinct lack of selenium intake in food.
Risk Factors
The risk factors of selenium are the things that can increase your chances of selenium deficiency, regardless of the situation of the soil in your area. These factors include the following:
- Digestive disorders like Cohen’s disease
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
- Dialysis treatment
All of these conditions impact the absorption of selenium in the body, even if the body is getting enough of it through diet.
Diagnosis of Selenium Deficiency
There is no single way to diagnose selenium deficiency because there is no test that measures its levels. That makes it difficult for doctors to diagnose the condition.
Nevertheless, doctors often measure glutathione peroxidase in the body, which is the enzyme that needs selenium in order to function properly. Low levels of this enzyme indicate selenium deficiency.
Treatment for Selenium Deficiency

Picture by Samarth Singhai at Pexels
Treatment for selenium deficiency mainly involves eating foods rich in selenium or taking the substance in supplemental form. The following foods are recommended by the National Institute of Health to increase selenium intake: whole wheat bread, beans, rice, yellow tuna, organ meats, and Brazil nuts.
Furthermore, the recommended amount of selenium by the National Institute of Health for people over the age of 14 is 55 micrograms (mcg) every day. Lactating or pregnant women should take at least 70 mcg of selenium per day.
The maximum amount of selenium you should be taking is 400 mcg per day. If your selenium intake is too high, you will feel a metallic taste in your mouth and an odor similar to garlic on your breath.
The issue with taking selenium through diet alone, when you are deficient, is that the amount of selenium in a specific food source varies greatly, depending upon where it was grown. For example, according to a 2017 study by E.C Silve Jr. and their team, a Brazil nut grown in one region can provide 288 percent of the daily value of selenium while the same nut grown in another region provides only 11 percent.
That is why selenium supplements can be helpful in fighting its deficiency.
Selenium supplements can be highly effective in fighting selenium deficiency in the body. It is important to note that the Food and Drug Administration does not monitor and regulate supplements as they do drugs. That is why it is vital that you buy supplements only from well-reputed and established companies.
Benefits of Selenium
After exploring the issues with selenium deficiency, this section outlines the various benefits of improving your selenium intake.
Antioxidant Action
One of the most prominent activities of selenium in the human body is its antioxidant action. Antioxidants are substances that help protect cells from getting damaged by the actions caused by free radicals.
These free radicals are left behind by different processes in the body such as metabolism. While useful for many processes, an excess of free radicals can cause oxidative stress, a process that harms the healthy cells in our bodies.
Oxidative stress plays a role in a range of conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, an increased risk of stroke, premature aging, cancer, and Alzheimer’s.
Selenium, like other antioxidants, helps decrease oxidative stress in the body by controlling the population of free radicals.
They protect cells from cell damage that oxidative stress may have caused by eliminating it at the source i.e., free radicals.
Reducing the Risk of Some Cancers

Picture by SHVETS production at Pexels
Selenium has the ability to decrease the risk of certain types of cancer. According to a review of over 167 articles published about selenium, the element performs four functions that help in the reduction of cancer. These functions include:
- Destruction of cancer cells.
- Boosting the immune system.
- Decreasing oxidative stress.
- Reducing DNA damage.
Another review of 69 studies established that high levels of selenium in the blood were connected to having a lower type of multiple types of cancers such as prostate, colon, lung, and breast cancers.
Other than that, oral supplementation of selenium is also associated with the reduction of symptoms born out of radiation sickness and other cancer treatments that have adverse impacts on the body. A study showed that selenium supplements help women with uterine and cervical cancers reduce the symptoms of radiation-induced diarrhea.
Cardiovascular Benefits
Low levels of selenium are associated with a pronounced risk of various cardiovascular diseases. That is why a selenium-rich diet can help keep heart disease at bay.
In a study conducted by Gemma Flores-Mateo and her team, it was found that increased levels of selenium are associated with a reduction in heart disease. To be accurate, a 50 percent increase in selenium intake decreases heart disease by around 24 percent.
One of the biggest factors that contribute to heart disease is inflammation. Selenium helps lower inflammation in the body, thus decreasing the risk of heart diseases.
In a systematic review of 16 studies involving over 430 thousand patients with heart diseases, selenium supplements helped decrease C-reactive protein, which is one of the major markers of inflammation.
Thus, the way selenium manages the risk of heart diseases is through lowering inflammation.
Other than that, selenium also helps decrease the risk of buildup of plaque in arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis. This condition can lead to further heart complications such as heart attacks, strokes, and other heart diseases.
Other Benefits
Other than the benefits mentioned above, selenium provides a range of other benefits as well. Some of them are mentioned as follows:
- Selenium is useful in preventing mental decline through neurodegenerative ailments such as Alzheimer’s disease. Selenium helps fight oxidative stress, which is believed to be involved in Alzheimer’s disease. People with Alzheimer’s disease show low levels of selenium in the blood.
- The substance is also vital for thyroid health. Studies have shown that thyroid tissue contains more selenium than any other part of the body. Thyroid health is important for the proper functioning of growth processes and metabolism.
- Another benefit of selenium comes in the form of its benefits to the immune system. Selenium boosts the immune system and helps fight against diseases. Selenium deficiency can render the immune system slow while various cells face serious damage in the absence of selenium.
- Selenium may also be effective in alleviating asthma symptoms. Asthma is linked with high inflammation and oxidative stress, two causes directly affected by selenium. A study has shown that asthma patients with low levels of selenium had worse lung function as compared to those with high levels.
Thus, the benefits of selenium are far-reaching and wide-ranged.
Frequently Asked Questions
Following is the list of most frequently asked questions about selenium.
1. Is it safe to consume selenium?
If taken in the recommended dosages, selenium is perfectly safe.
2. What are the recommended dosages of selenium?
The recommended dose ol selenium for an adult is around 55 mcg. It must be noted here that you should never take more than 400 mcg. Otherwise, it can lead to selenium toxicity which can be quite dangerous.
3. How to detect selenium toxicity?
If you have been taking more than 400 mcg of seleneium, look for the following symptoms of selenium toxicity:
- Muscle soreness
- Tremors
- Facial flushing
- Nausea
- Dizziness
- Hair Loss
If selenium toxicity is acute and goes untreated, it can cause kidney failure, heart attack, and even death.





 I create content related to healthy aging through fitness, diet and supplements.
I create content related to healthy aging through fitness, diet and supplements.

